Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
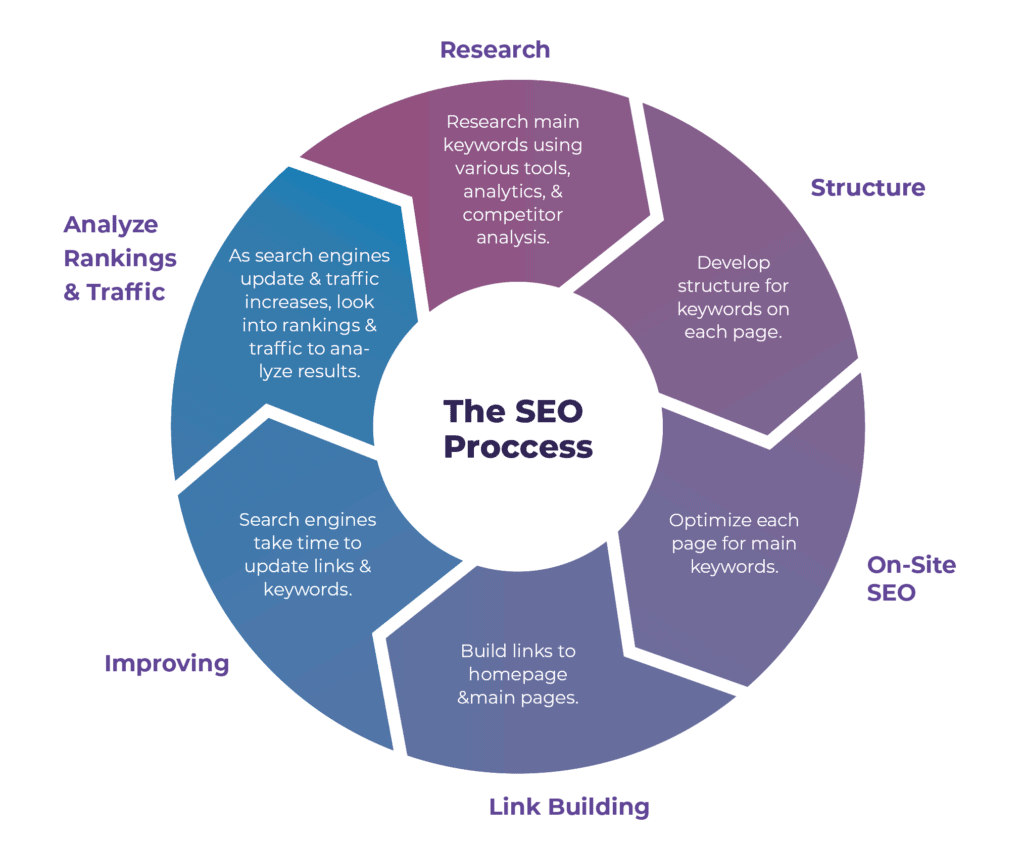
What are factors for SEO Ranking?
Google and other search engines keep their algorithm a guarded secret. However there are ONSITE and OFFSITE factors that can help drive traffic to your site and boost your ability to be discovered during a search.
ONSITE FACTORS | OFFSITE FACTORS |
Keywords Site content Meta-tags Title tags Alt-tags Sitemap (having a site map on the site increases ranking) URLs Headings | Inbound linking (number of sites linking to you) External linking (number of links from your site to others) Directory registrations |
Keywords
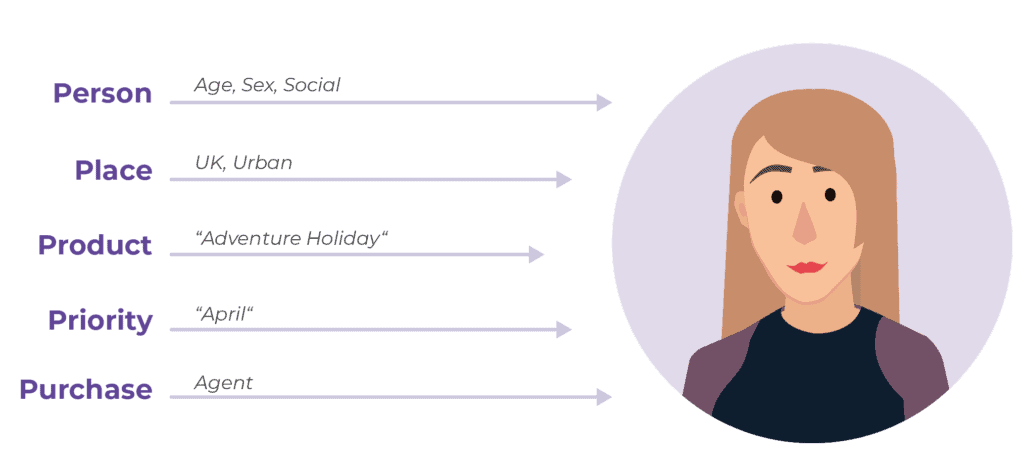
Our searches reveal who we are. Each time a user searches they are revealing data and information to the browser. This is stored and used to deliver relevant content back. Each search provides information on:
- Person: who the user is, it segments and qualifies them
- Place: location of the searcher as well as their destination
- Priority: the search is an indicator of their timeframe
- Product: indicator of what exactly is important to searcher
For example: A person is looking at going on holiday, she opens Google and searches for “Adventure Holidays”. She does the search via her personal phone. Based on her previous purchases, her social media use and her location, the search engine knows a lot about the person making the search.
A keyword is a significant word or phrase relevant to the content of your website and they are the commonly used keywords users type into a search engine to find you. Keyword research is finding the search phrases your customers commonly use. There are two forms of keyword research: online and off-line. In the previous module on content creation and in module 3: Understanding your Target Audience, much of the offline keyword research has been done.
Online Keyword research tools allow you to perform filtered keyword research according to following criteria:
- Custom date ranges
- Query volume
- Historical trends
- City/country/global
- Levels of data
- Related phrases
Keyword research
Keyword research is the process of discovering words and phrases that people use in search engines with the ultimate goal of optimising content around those terms and ranking for those terms in search engines.
Researching keywords help you figure out the thoughts, fears, and desires of your target market. That is because keyword research gives you insight into what customers are searching for, and the exact words and phrases that they use. Keyword research is market research for the 21st century.
Keyword Research is a two-step process:
- Brainstorm: Use a paper and pen to come up with a few ideas of what you think people will search for to find your website. These are not keywords, rather they are topics you cover.
- Use Keyword Tools to discover Keywords based on your brainstorm.
Using keyword tools
There are many free and paid keyword tools available. In this section we will identify a few tools and hacks to do keyword research.
- Word Tracker www.wordtracker.com
- Wordstream www.wordstream.com
- Google Ads: This has a keyword research tool in the app
- SEM Rush (Paid)
- Keyword IO: This tool helps to search how a keyword is performing or trending in specific countries or regions in their local language https://keywordtool.io/.
Hacks
Google Ads are rather aggressive in trying to make you create an ad before you get to use the tools of Google ads. A simple hack is to do a Google search of the terms you came up with in your brainstorm. At the bottom of the SERP page Google offers 8 top searches for the term. This can be used to strengthen your keyword search.


Go to Assignment 7.2.6: Keyword research.
Onsite optimisation
To improve your organic search you need to ensure on-page optimization. On page optimisation is the process of refining your website so that it will be indexed and ranked by search engines favourably.
Things you can do to optimise your website:
- Keywords
- Content
- Meta Tags
- Sitemap
1. Keywords
In the section above, we looked at keywords as a broad topic. In this section we put those keywords to work. It is important to include the most relevant keywords in the content, meta tags and site supports of your site. This way your audience can find you. In the case of keywords, your audience are using these terms to find content that is relevant to them. Using keywords means that your site becomes more visible to those you wish to reach. You can see a visual example below on keyword placement in an article.

2. Content
Search engines favour websites that have unique, relevant and up-to-date content. “Content is King” when it comes to SEO. Content updates can contain a broad mix of content: text, photos, videos, slides etc.
In section 7.1 we explored content strategies. Creating exciting, engaging content starts by understanding the audience and building content that fills a need (knowledge, skill or attitude). Therefore we will not go into detail here on how to make content. Instead we will focus on:
- Content Layout
- Content frequency
- Content Balance
CONTENT LAYOUT
This is often forgotten in the world of SEO, but this is essential and can make a huge difference. Your web content should exist to answer searchers’ questions, to guide them through your site, and to help them understand your site’s purpose. Great content can get lost in bad page flow.
There are a few key questions you should answer:
- What goes on the page, in what order?
- What is the searcher trying to accomplish?
- What is the call to action I want the user to do?
SEO favours a page layout that is well crafted. It should include page headings, paragraph headings, paragraphs, bold text, links, images and/or video. These help in the crawling spiders to decide the relevance of your page. If it is in bold or in a heading, it probably means it is more relevant than a casual mention in the body of the text.
Your layout should try to achieve solving the searcher’s task (the thing they are trying to accomplish) quickly and enjoyably. The page should also serve as a way to get the user to your call to action quickly.

Top Tips:
- Most SEO specialists agree that 400 words on page would be considered quality content.
- Internal links are important in order to aid navigation, and search engine spiders to track the pages.
CONTENT FREQUENCY
Chronology and relevance are at the core of Search Engine Optimisation. A website that has remained dormant for weeks or months without an update is not that appealing to search engines. Search engines reward fresh relevant content, or refreshed content to reinforce relevance.
Google has long and short crawl spiders. Long crawl spiders seek out new content and pages every month whereas the short-term spiders crawl sites more frequently. The spiders love to discover new and up-to-date content as this usually means it’s more current and therefore more relevant.
The more frequently you post new, quality content to your site, the more likely your site is to rank higher. Many SEO specialists include blogs into websites as this allows more frequent content to be uploaded. Links to social media on site also ensure more constant content on site.
The “Freshness Algorithm” of Google and other search engines affect mostly news sites. This is the broader category, in which you can include celebrities, general news, politics, technology, etc. Usually Citizen Voice program themes would fall under the News category. Love Matters has far more evergreen content (related to the body, sexuality etc). This content doesn’t need to be fresh as its consistent.
It is important to note that sometimes publishing quality content frequently is not always possible. However there is content that can be refreshed or updated (evergreen content). By simply updating and republishing relevant quality content, you can increase the frequency score. However, this means that you need to have created a lot of content in the past.
CONTENT BALANCE
Keyword Stuffing is trying to fit all the keywords you have discovered as many times into a website as possible to increase your traffic. It is important to note that “Keyword Stuffing” is not advised. A good rule is, the keywords you use should seem natural to insert them into your content. You want to be able to strengthen your content with the keyword rather than just introducing random keywords that don’t add value to the content.
Keyword density is the percentage of times a phrase appears on a page, in relation to the total number of words on a page. You may, from time to time, come across sites that have very poor-quality content but are written to include as many keywords as possible. These “click bait” sites are not relevant to the user and often have high page bounce rates (the rate at which a user leaves the page when they discover content they are not looking for).
Generally, a page with 400 words is usually deemed a quality page.
3. Meta Tags
A webpage is made up of HTML (Hyper Text Mark-up Language). HTML is the programming language for web pages and contains several crucial elements for SEO. A relevant meta tag is an HTML element that provides information about the page.
TITLE TAGS
<title> tags appear in the title bar of the browser and are one of the factors used by search engines to determine the content of your page. Rather than including the company name in the <title> tag, use the keywords that your organisation wants to rank for. This will give your organisation a solid advantage for ranking in the search engines. Make sure to limit the <title> tags to 60 characters in length, including spaces, so that the full text of the title tags appears in the search engine rankings and doesn’t get cut-off by Google.
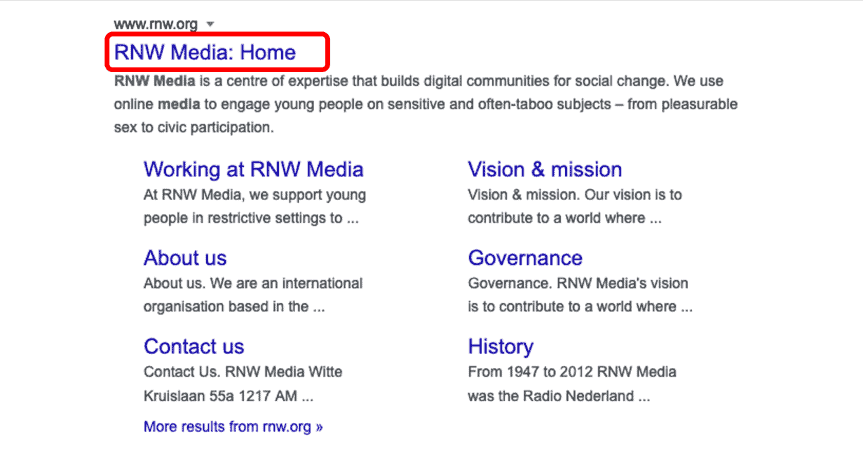
The Title tag is the most important on-page SEO factor. That’s because your title tag gives search engines a high-level overview of what your page is all about. Instead of “Home” as seen in the example, what could the text read? An optimal title tag should include two to three of the most important keywords for your page.
DESCRIPTION TAGS
Description tags are what appear in the search engine results pages – they give the web user an overview of what the site is about. Put your marketer’s hat on and write a description that convinces users to click on the result. This is your site’s first opportunity to attract visitors, so it is vital that you give your organisation the best chance of standing out from the other results.
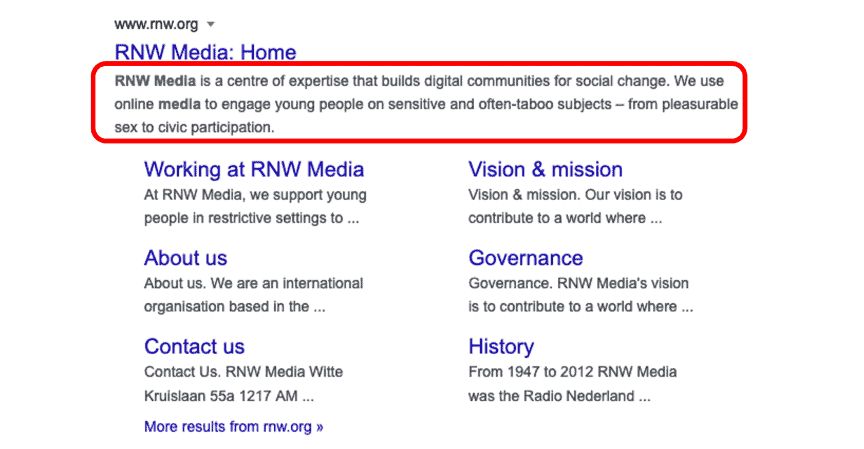
Remember, Google also uses meta description tags to differentiate web pages (although not as much as title tags) so you also need to be careful to describe each page differently to avoid any duplicate content issues. Including free offers, guarantees and a phone number can improve the click through rate on your clients’ SEO ranking.
Make sure to limit the <meta> description tags to 160 characters in length, including spaces.
ALT-TAGS
Alt-tags are tags that are used to describe rich content like images and video. Crawling spiders cannot understand what is in an image or video (although this is getting more advanced). It is therefore necessary to tell the search spiders what the image or video contains or is about through the use of alt-tags. Alt tags are descriptions.
It is also a good place to introduce keywords into the code and can help boost SEO. If you want images on your site to rank higher and appear more often in Google Image search you can also include more general keywords.
4. Sitemap
A sitemap is a page on your website that provides a map of the website structure in the form of text links to all other pages. The function of a sitemap is to help search engines to find your pages. The site map should link to every page on your site and every page should link to it. A sitemap xml: facilitates crawling, indexing, ranking.
Offsite optimisation
Off-page optimisation is primarily concerned with improving your website ranking. Ranking is the position of the website in search results based on the number and quality of all websites that link to your page. Pages are ranked by assessing the popularity or ranking of the pages that link to you.
Link building
A hyperlink or link is a reference to a website or page, that users can follow in order to navigate the web. There are two elements to a link:
- link text: the text that appears on the page
- link URL: the destination that clicking the link will take you to
An internal link is a link from one page on your website to another page of your website. An inbound link is a link from another website to your website. They are also called backlinks.
Inbound links are especially valuable for SEO because they represent a “vote of confidence” from one site to another. In essence, inbound links to your website are a signal to search engines that others vouch for your content. If many sites link to the same webpage or website, search engines can infer that content is worth linking to, and therefore also worth surfacing on a SERP. So, earning these inbound links can have a positive effect on a site’s ranking position or search visibility. There is a quality scale to link sources:
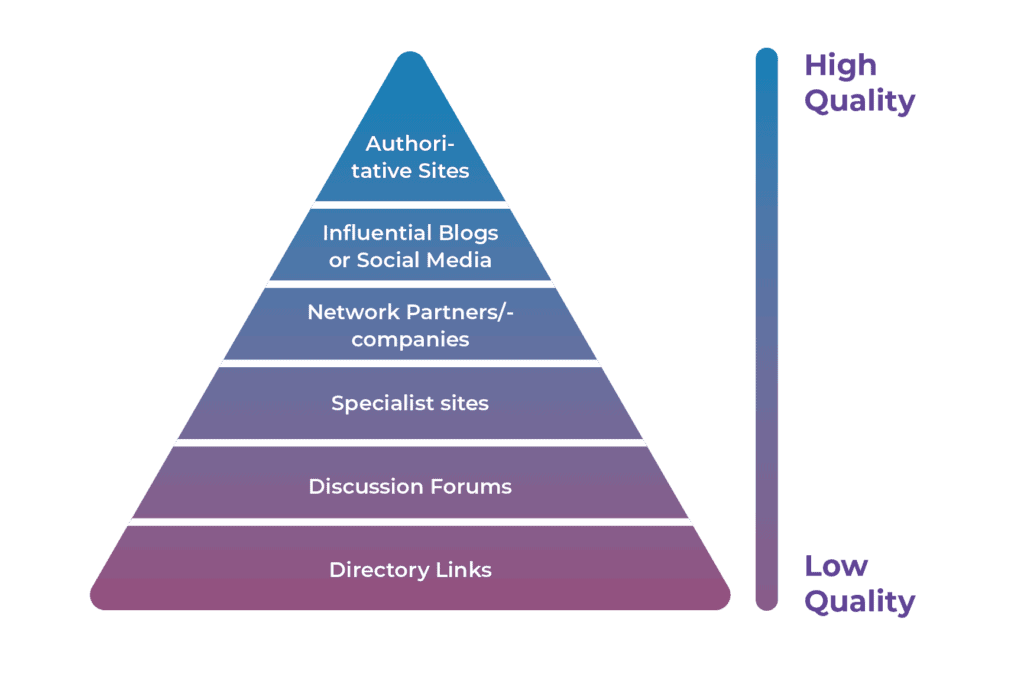
Link building techniques
Link building happens primarily through content link building techniques such as creating articles, blog posts, videos, infographics for publication and content that is made for distribution on other websites. These content pieces then connect to your various site pages or your campaign.
- Directories link building is the submission of listings, press releases or product catalogues to directories. These could also include services that are offered through partners. Oftentimes there are networking organisations such as Partos, Forum Syd, GMFD and numerous other that have directories of organizations that they work with. These directories need to be kept updated with information as well as latest links.
- CSO/NGO Partner organizations could link to each others websites and find ways to collaborate and build links between their sites. Link building could also be through sponsorship and promotions, sponsoring activities/charities/running competitions.
- Social Link Building is links from social media to your website and vice versa. Ensure you have presence on all major online platforms (social media, You Tube, Twitter, Facebook) as your listing there may be found in search before your own website. Links within social networks are being included by search engines as influences of ranking.
Be cautious of link buying offers, as paid links are generally in violation of search engine quality guidelines. Flash content, keyword stuffing, duplicate content, broken links and no follow tags are all ways that link building can be adversely affected damaging to SEO.
Link formats
The links you build can have different formats. These include:
- Uninformative link: Click here
- URL link: www.rntc.com
- Topic link: Media Training
- Keyword link: Countering Disinformation Training RNTC (and ensure variety of keywords.)
