Digital Optimisation to Support Engagement Copy
After learning about different moderation techniques, how to navigate online and create campaigns for more engagement, it is time to look at the more technical part of how to serve content to your audience. More specifically, this final unit will look into how digital optimisation through Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) works to ensure more relevance and greater engagement.
Nothing is “techier” than a TLA (a three-letter acronym) and there are many in the world of digital marketing and building digital communities. Two that are very common in the work of RNW Media are SEO and SEM. What do they mean and how are they different? The video below can help shed some light on these terms:
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is the process of refining your website so that it will be indexed and ranked by search engines, as well as leveraging your links from other sites. In simpler terms, it’s a way to be seen on search engines like Google.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is the practice of marketing a business using paid advertisements that appear on search engine results pages. These use Pay Per Click (PPC) adverts in the search engine to drive traffic.
Both SEO and SEM are fundamental parts of any online marketing strategy. For a media for behaviour change organisation like RNW Media, the “business” includes vital information and services for young people in restrictive settings. We do not market traditional products but rather our information and services. We wish to make these services and information visible to our audience and because we believe our content to be of high value, we want them to find us before the user finds a misinformation or disinformation.
How search works
Watch this video from Google on how their page ranking works and this one on searching for lasagna.

Go to Assignment 7.2.5: Which factors affect ranking?
Why page ranking is important
When a search is performed in any search engine, the search engine produces a Search Engine Response Page (SERP). This page usually has the most relevant responses from the search engines’ index of the web. Each search engine will have a different recipe for serving up its most relevant pages. You can test this out by seeing what different SERPs are returned for searching the same term in different browsers.
There are two types of rankings: Organic and Paid. It is likely that you are familiar with this type of page:
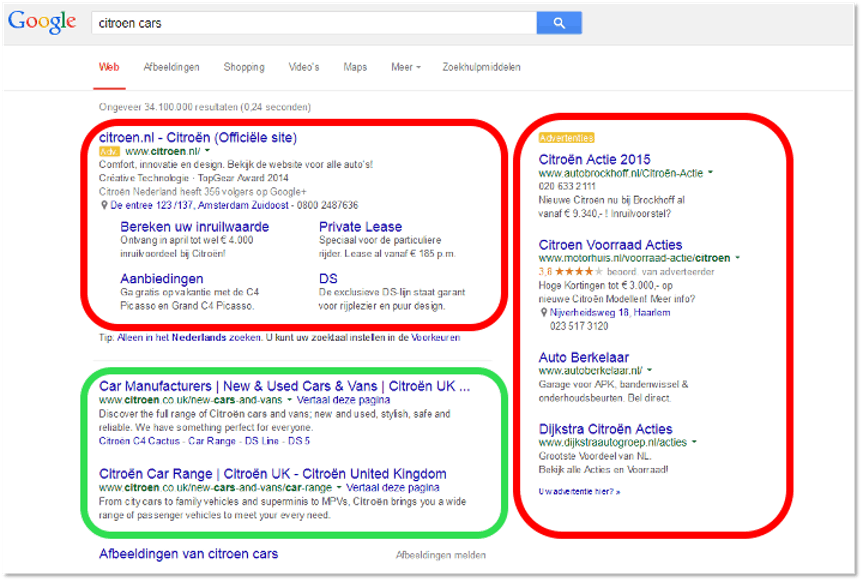
The areas on the SERP marked in red are “paid” responses. The areas marked in green are the “organic” responses. 30% of Users click on the “paid” sections of the SERP. 70% of users click on the “organic” parts of the SERP, usually in the first three or four pages that are listed.

- Page 1 of Google captures a whopping 95% of all traffic.
- The top result on page 1 of Google receives about 32.5% of the overall traffic; the second entry receives 17.6%, while the 7th entry on page 1 of Google sees only 3.5%…and the downward slide continues all the way to page 2 and beyond.
- The top 10 queries on the SERPs enjoy an average click-through rate of 208%, meaning searchers click more than twice on average on the first page.
- Traffic drops by 140% when you move from the 10th position (bottom of page 1) to the 11th position (top of Page 2).
SEO is the process of improving your chances of being indexed higher by search engines. It is important to note that Google SEO is the most important as it constitutes 77% of all web search in the world. Baidu, the Google equivalent in China, is third after Bing.
In digital marketing terms, any organisation must jump through 3 hoops in attempting to engage with potential customers through search engines. The key to understanding search engine results is summed up in one word: relevance.
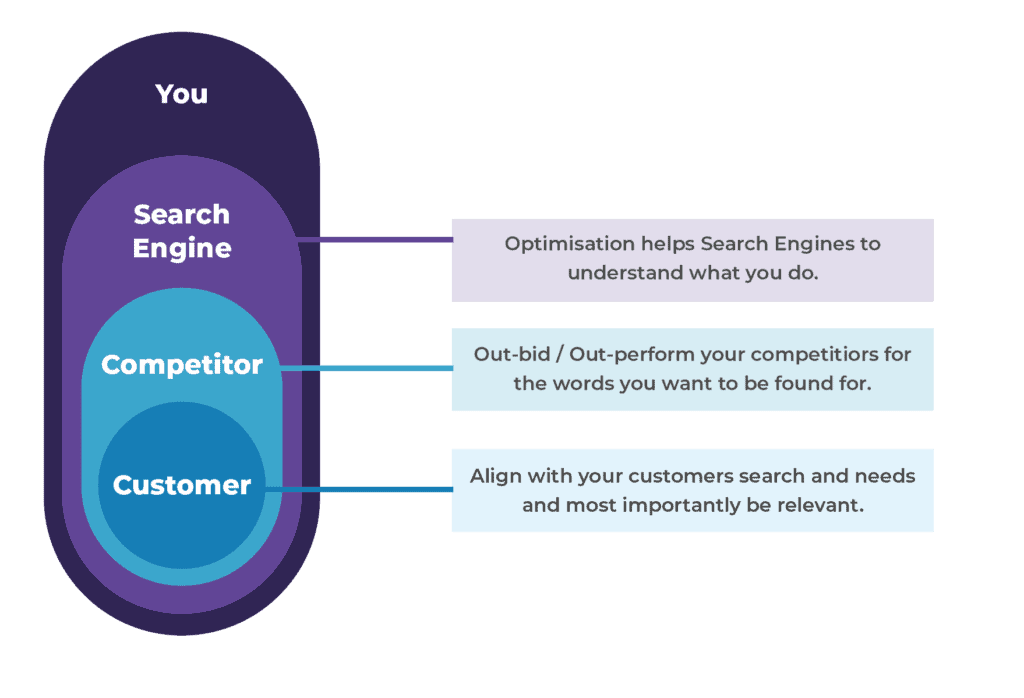
Why RNW Media needs high ranking pages
Being discoverable on the internet is essential as an NGO that has a focus on delivering information to users. When young people search for information on the internet they may be exposed to good information or bad, damaging information. Take for example the Love Matters programme. Young people have many questions about their bodies and sex. Usually, the highest returned searches include pornography due to the search terms that are used. This may have negative or harmful consequences on body image or key understanding of concepts of sex and sexuality.
Search results are affected by location. Certain search terms are also highly polarised and if you search for a polarising idea to learn more about this, a SERP may yield a result that is one sided and, in some cases, dangerous. Consider the topic “abortion” in some parts of the world, what may be returned are many “guilt and shame sites” from a conservative point of view and not fact-based information. This may dissuade a young person from accessing services or important information.
Educational Institutions, Civil Society Organisations (CSOs) and NGOs are considered more trusted sources on Google’s search algorithm. This means that they will automatically rank slightly higher. This also means that competing NGOs or CSOs will also be visible in the SERP. It is important to rank above competitors in the SERP page.
Benefits of high listing position in organic search
For your visibility
Increased click through
Increased engagement
Increased conversions
For your reputation
Increased visibility
Enhanced reputation
Credibility and status
Market leadership
Competitive advantage
